【Java】円同士の当たり判定
本稿はJavaで円同士の当たり判定を実装する方法を紹介します。
円同士の当たり判定の実装方法
円同士の判定をするjava標準APIは見つけられなかったので自力で実装してみようと思います。
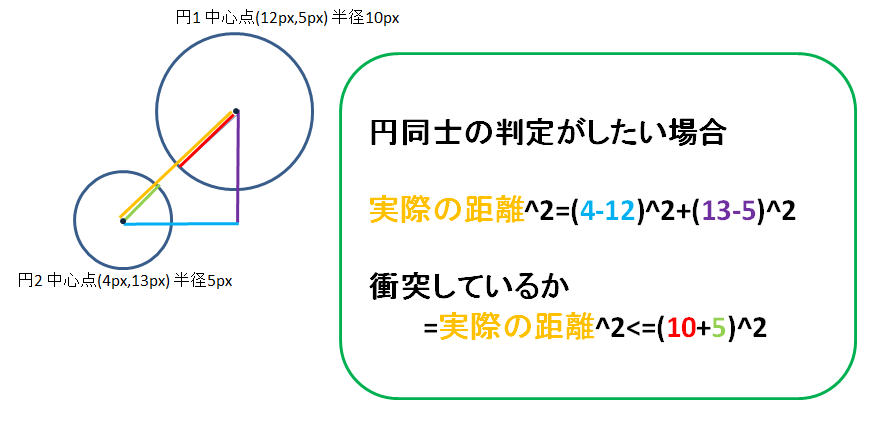
円同士の判定をするには二つの円の中心点からの半径の長さを加算したものが実際の距離よりも短ければ、衝突したという判断ができます。
半径の長さはプログラマが自由に決めるのですぐに求められます。
では円の実際の距離を算出するにはどうするのかというと、ピタゴラスの定理を使用します。
ピタゴラスの定理とは
【 距離 ^ 2 = X座標距離 ^ 2 + Y座標距離 ^ 2 】
を表す公式です。
この公式を利用することで二点間の距離を求めることができます。
となると、中心点のX、Y座標がわかれば実際の距離を求めることができそうです。
中心点の座標はプログラマが自由に決めることができるので、すぐに計算できます。
[Xの距離^2+Yの距離^2]ができれば[距離^2]が求められるので、[(円2.x-円1.x)^2+(円2.y-円1.y)^2]の計算をすればよさそうです。
算出できたらMath.sqrt(算出結果)とすれば距離を求められそうです。
しかし、このsqrtメソッドは重いといわれているので使用せず、距離^2のまま判定します。
距離が短いかどうかを判定するだけなら正確な距離を出す必要はないからです。
代わりに、半径を加算した値を二乗して比較します。
それではサンプルをご覧ください。
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//円1を定義
int cx1= 100,cy1=100,r1=50;
//円2を定義
int cx2= 150,cy2=150,r2=50;
//実際のX,Y距離
int vx = cx2-cx1;
int vy = cy2-cy1;
//半径同士を加算した距離
int v = r1+r2;
//判定
System.out.println(vx*vx+vy*vy<=v*v);
}
}
true
実際にアニメーションさせながら判定できているか確かめる
いつも通り、わかりやすいアニメーションサンプルを実際のソースとともにご覧ください。
今回は円を表すクラスを自作し、intersectsメソッドを定義して判定するように実装しました
import java.awt.Color;
import java.awt.Font;
import java.awt.Graphics;
import java.awt.Graphics2D;
import java.awt.Insets;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import javax.swing.JPanel;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TestWindow tw = new TestWindow("テスト", 400, 300);
tw.change(new DrawCanvas());
tw.setVisible(true);
tw.startGameLoop();
}
}
//ウィンドウクラス
class TestWindow extends JFrame implements Runnable{
private Thread th = null;
private double sleepAddTime;
private int fps=60;
public TestWindow(String title, int width, int height) {
super(title);
setDefaultCloseOperation(EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
setSize(width,height);
setLocationRelativeTo(null);
setLayout(null);
setResizable(false);
setFps(fps);
}
public synchronized void change(JPanel p) {
getContentPane().removeAll();
Insets inset = getInsets();
p.setBounds(-inset.left,-inset.top,getWidth(),getHeight());
add(p);
validate();
repaint();
}
public synchronized void startGameLoop(){
if ( th == null ) {
th = new Thread(this);
th.start();
}
}
public synchronized void stopGameLoop(){
if ( th != null ) {
th = null;
}
}
public void run(){
double nextTime = System.currentTimeMillis() + sleepAddTime;
while(th != null){
try{
long res = (long)nextTime - System.currentTimeMillis();
if ( res < 0 ) res = 0;
Thread.sleep(res);
repaint();
nextTime += sleepAddTime;
}catch(InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public void setFps(int fps){
if ( fps < 10 || fps > 60 ) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("fpsの設定は10~60の間で指定してください。");
}
this.fps = fps;
sleepAddTime = 1000.0 / fps;
}
}
//移動アニメーション用クラス
class VertexMove2D{
private double x;
private double y;
private final int[] xpoints;
private final int[] ypoints;
private final int npoints;
private boolean isInvert;
private int currentPoint;
private int nextPoint;
private int speed;
private double mx;
private double my;
private double checkValue;
public VertexMove2D(int[] xpoints, int[] ypoints, int npoints, int speed, int initPoint) {
this.xpoints = xpoints;
this.ypoints = ypoints;
this.npoints = npoints;
this.speed = Math.abs(speed);
this.isInvert = speed < 0;
this.currentPoint = isInvert ? initPoint + 1 : initPoint - 1;
prepareNext();
}
private void prepareNext() {
if ( isInvert ) {
int currentPoint = this.currentPoint - 1;
if ( currentPoint < 0 ) currentPoint = npoints - 1;
this.currentPoint = currentPoint;
int nextPoint = currentPoint - 1;
this.nextPoint = nextPoint < 0 ? npoints - 1 : nextPoint; } else { int currentPoint = this.currentPoint + 1; if ( currentPoint >= npoints ) currentPoint = 0;
this.currentPoint = currentPoint;
this.nextPoint = (currentPoint + 1) % npoints;
}
int sx = xpoints[currentPoint];
int sy = ypoints[currentPoint];
int ex = xpoints[nextPoint];
int ey = ypoints[nextPoint];
int vx = ex - sx;
int vy = ey - sy;
double rad = Math.atan2(vy, vx);
mx = Math.cos(rad) * speed;
my = Math.sin(rad) * speed;
checkValue = vx * vx + vy * vy;
x = sx;
y = sy;
}
public void draw(Graphics g) {
g.drawPolygon(xpoints, ypoints, npoints);
}
public void fill(Graphics g) {
g.fillPolygon(xpoints, ypoints, npoints);
}
public void move() {
double xx = x + mx;
double yy = y + my;
int sx = xpoints[currentPoint];
int sy = ypoints[currentPoint];
double vx = sx - xx;
double vy = sy - yy;
if ( checkValue <= vx * vx + vy * vy ) {
prepareNext();
} else {
x = xx;
y = yy;
}
}
public void invert() {
isInvert = !isInvert;
}
public boolean isInvert() {
return isInvert;
}
public int getSpeed() {
return speed;
}
public void setSpeed(int speed) {
if ( speed < 0 ) {
invert();
speed = -speed;
}
this.speed = speed;
}
public double getX() {
return x;
}
public double getY() {
return y;
}
}
//円を表すクラス
class Circle {
public double radius;
public double cx;
public double cy;
public Circle(double cx, double cy, double radius) {
this.cx = cx;
this.cy = cy;
this.radius = radius;
}
public boolean intersects(Circle circle) {
return intersects(circle.cx, circle.cy, circle.radius);
}
public boolean intersects(double cx, double cy, double radius) {
double vx = cx - this.cx;
double vy = cy - this.cy;
double vr = radius + this.radius;
return (vx*vx+vy*vy) <= vr*vr;
}
}
class DrawCanvas extends JPanel{
int[] x = {60,150,280,340,270,160,90,70};
int[] y = {80,200,90,120,150,250,240,260};
//図形の頂点を移動するオブジェクト。
VertexMove2D m1 = new VertexMove2D(
x
,y
,8//頂点の数
,2//移動速度
,0//配列の0番を開始地点に
);
//もう一つの図形の頂点を移動するオブジェクト。
VertexMove2D m2 = new VertexMove2D(
x
,y
,8//頂点の数
,-3//移動速度
,4//配列の4番を開始地点に
);
Circle r1 = new Circle(100, 100, 50);
Circle r2 = new Circle(100, 100, 50);
public void paintComponent(Graphics g){
super.paintComponent(g);
Graphics2D g2 = (Graphics2D)g;
g.setColor(Color.RED);
g2.drawOval((int)(r1.cx-r1.radius),(int)(r1.cy-r1.radius),(int)(r1.radius*2),(int)(r1.radius*2));
g.setColor(Color.BLUE);
g2.drawOval((int)(r2.cx-r2.radius),(int)(r2.cy-r2.radius),(int)(r2.radius*2),(int)(r2.radius*2));
g.setColor(Color.GREEN);
m1.draw(g2);
m1.move();
r1.cx = m1.getX();
r1.cy = m1.getY();
m2.move();
r2.cx = m2.getX();
r2.cy = m2.getY();
g.setFont(new Font(Font.MONOSPACED,Font.BOLD,20));
//円同士の当たり判定
if ( r1.intersects(r2) ) {
g.setColor(Color.RED);
g.drawString("当たっています", 50,50);
} else {
g.setColor(Color.BLUE);
g.drawString("当たってません", 50,50);
}
}
}
これでちゃんと当たり判定ができていることが確認できました。




ディスカッション
コメント一覧
まだ、コメントがありません